| Version 23 (modified by , 13 years ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
PySide for Android
This guide describes:
- how to build Shiboken & PySide for Android using the Necessitas SDK
- how to use the resulting libraries
- and how to bundle them with your Python program in a standalone APK
NOTE: If you just wan't to run you Python & PySide programs on Android, you can skip the Building PySide section and go directly to PySide for Android example application & Example project for the Necessitas Qt Creator
Do you see something incorrect or missing from the guide ? Let me know, so I can fix it ! :)
Building PySide
Preparation
First install the prerequisites:
- Necessitas SDK
(make sure you have the Android SDK platform 14 installed in it)
- system-wide installed Shiboken
- system-wide installed Python 2.7
- Python 2.7 compiled for Android
- cmake
- git
This command should probably fetch most of the prerequisites on Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install build-essential cmake git python2.7-minimal shiboken
If you find some are is missing or if you wan't to provide similar command for other distributions, let me know ! :)
Then clone the Android-pyside-build-scripts project and cd to it's directory:
git clone git@github.com:M4rtinK/android-pyside-build-scripts.git cd android-pyside-build-scripts
Now run the prepare.sh script:
./prepare.sh
It clones Android-modified Shiboken & PySide and creates some folders needed for the build.
And that's it, you are ready to start the build. :)
Build
To start the build, just run the main build script, called build.sh:
./build.sh
It first builds Shiboken, followed by PySide. The script is fully automatic, but waits for the user to press any key:
- after Shiboken is configured for build
- after Pyside is configured for build
Like this you can easily check for any errors during configuration.
Also note, that when running the script, it clears any previous build results before building.
You can also run the build_shiboken.sh and build_pyside.sh scripts manually, just always make sure to run the Shiboken one before running the PySide one.
Results
The resulting PySide libraries compiled for Android are located in the stage/lib folder.
See the Example project for the Necessitas Qt Creator section for how the PySide libraries can be used as a part of a self-contained Android application.
PySide for Android example application
This is an example, that demonstrates a fully functional standalone Android application that uses Python, PySide and Qt Components.
Ready-to-install APK
A ready-to-install standalone APK is available here:
http://modrana.org/platforms/android/pyside_example/PySideExample_1.1.apk
Just install it and press the PySideExample icon.
First start
If haven't yet installed any Ministro using Qt application on your Android device, you will be redirected to the Play store to install the Ministro application. Ministro is a manager & updater for the Qt libraries for Android. The example application requires to be installed to run. So just install Ministro and everything else will be handled automatically. You might need to press the PySideExample icon again once Ministro is installed.
Once Ministro is installed and does it's work, the example might still take some time to start, as it is unpacking Python, Qt Components, theme for Qt Components and the example program to it's working directory. Once the unpacking is finished, the example application will be started.
The unpacking is done only once on the first application start, following starts are very fast, at least when tested on my device (HP Touchpad with CM9).
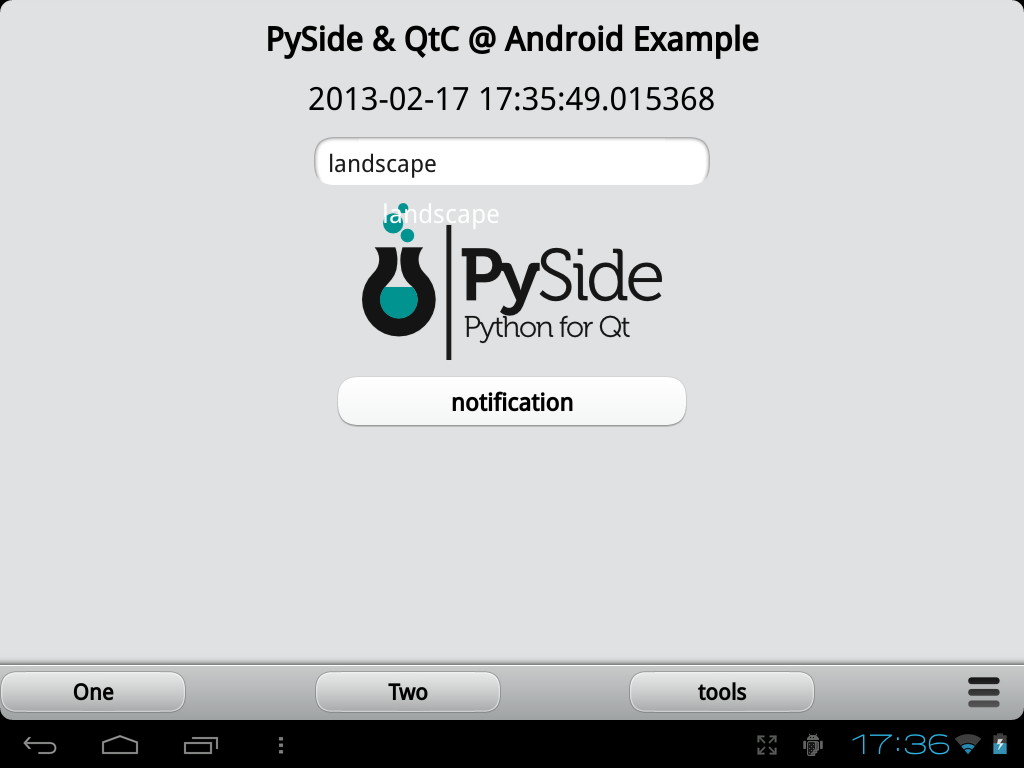
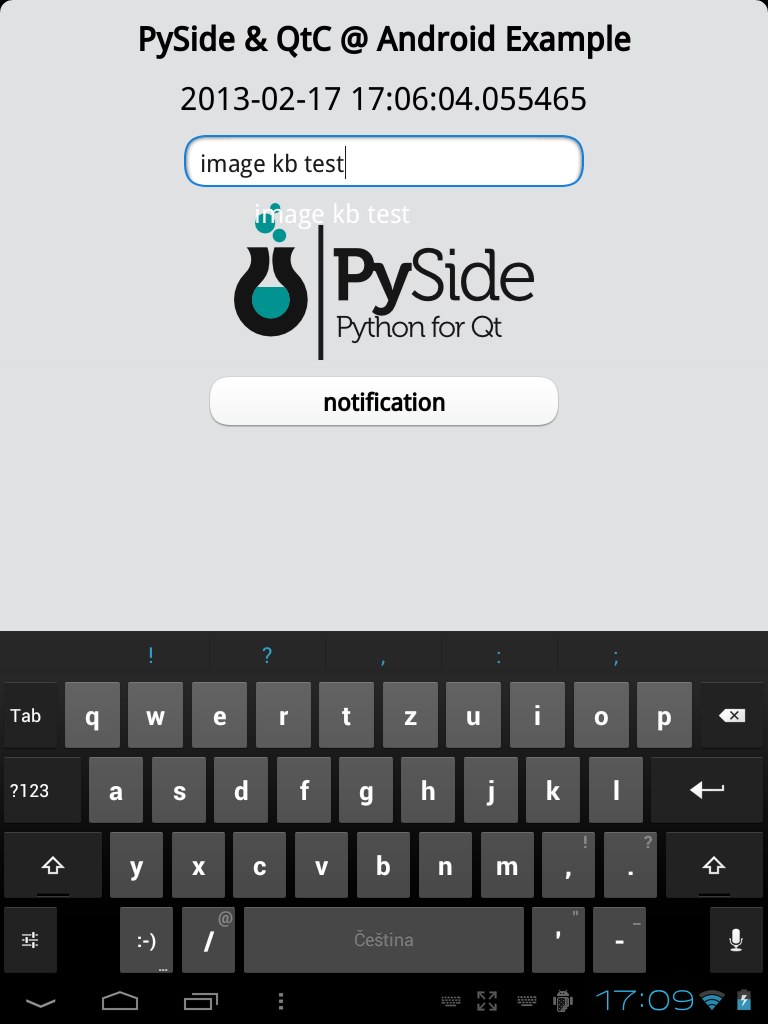
What the example application demonstrates
- sending data to Python and back
- the content of the entry fild is sent to Python, where it is painted on the PySide image and returned to QML using ImageProvider
- the date is retrived in Python and shown in QML
- working text entry with the Android virtual keyboard
- working screen rotation
- correct Portrait/Landscape orientation switching
- in both normal & inverted orientations
- working notifications (InfoBanner)
- working ToolBar
- working Menu
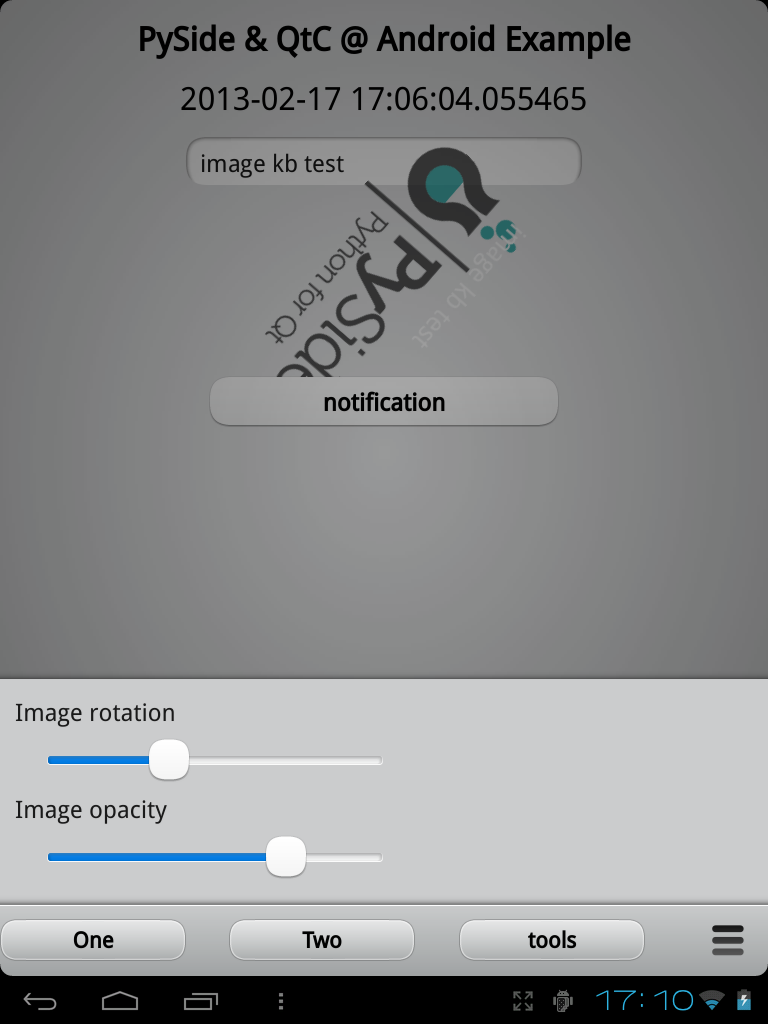
- "tools" menu with rotation & opacity sliders for the PySide image
Source code
Available from Github under BSD licence:
https://github.com/M4rtinK/expyside/tree/android
Size of the APK
The example APK has about 16 MB. This is because it needs to bundle quite a lot of libraries and related files. Big part of it is actually not used by the example in any way.
For normal applications it should be possible to make the resulting APK much smaller by:
- includding only the PySide libraries that are actually used
- removing unused Python modules
- cutting down the Qt Components theme from all grahics & icons that are not used
Example project for the Necessitas Qt Creator
This project has been used to generate the above mentioned application example APK.
Using the project
Using the project to build your own project is very easy. Just install the Necessitass SDK and clone the example project from git:
git clone git://github.com/M4rtinK/android-pyside-example-project.git
Then just open the PySideExample.pro with the Necessitas Qt Creator.
To generate a new APK, just click the green "deploy" button - Qt Creator should rebuild the the APK and deploy it either to the simulator or to any connected Android device that has debugging enabled.
How does it work ?
The project contains various components, that together enable the creation of fully standalone Python & PySide application APK, while also allowing to bundle any arbitrary libraries and files needed by the application.
The example project is called PySideExample and uses the org.modrana.PySideExample unique name. this means, that when it's APK is installed on and Android device, it gets installed to this directory:
/data/data/org.modrana.PySide.Example/
This path is important, as the application needs to set a couple of environmental variables during startup, pointing to libraries and themes that reside in this directory.
C++ wrapper
The main.cpp and main.h files are used to build a C++ Python wrapper. This wrapper is build against the the Android-compiled python libraries in build_dependencies/python by Necessitas.
Once the APK is deployd to the device and started, this wrapper is run. It initializes it's build-in Python interpreter, which tries to start the /data/data/org.modrana.PySide.Example/main.py Python file. This Python code then imports PySide, instantiates a QApplication and starts the main loop.
Behind the scenes, Necessitas handles wrapping the QApplication to an Android activity and showing it on the screen. It also handles other stuff like keyboard input & Qt Mobility.
main.h
This file contains important paths for the C++ wrapper.
#ifndef MAIN_H #define MAIN_H #define MAIN_PYTHON_FILE "/data/data/org.modrana.PySideExample/files/main.py" #define PYTHON_HOME "/data/data/org.modrana.PySideExample/files/python/" #define PYTHON_PATH "/data/data/org.modrana.PySideExample/files/python/lib/python2.7/lib-dynload:/data/data/org.modrana.PySideExample/files/python/lib/python2.7/:/data/data/org.modrana.PySideExample/files/python/lib/python2.7/site-packages:/data/data/org.modrana.PySideExample/files/python/lib" #define LD_LIBRARY_PATH "/data/data/org.modrana.PySideExample/files/python/lib:/data/data/org.modrana.PySideExample/files/python/lib/python2.7/lib-dynload:/data/data/org.kde.necessitas.ministro/files/qt/lib/" #define PATH "/data/data/org.modrana.PySideExample/files/python/bin:$PATH" #define THEME_PATH "/data/data/org.modrana.PySideExample/files/python/themes/" #define QML_IMPORT_PATH "/data/data/org.modrana.PySideExample/files/python/imports/" #endif // MAIN_H
MAIN_PYTHON_FILE- path to the main Python file to run once the application is startedPYTHON_HOMELD_LIBRARY_PATH- : separated list of paths used to look for libraries when loading themPATH- search path for executablesTHEME_PATH- path to the main themes folder for Qt ComponentsQML_IMPORT_PATH- path to the Qt Componentsimportsfolder
main.cpp
This is the C++ wrapper, it contains the embedded Python interpreter that is used to start the application and also sets some important environmental variables specified through main.h .
The example Python application
Bundling
Modified QtActivity
my_python_project.zip
python27.zip
Modifying the project
When you want to use the example project as basis for your Python application for Android, you just need to rename it and replace the example application.
But just in case I've also documented replacing all the other components.
Renaming
Replacing the application
The application is located in: android/res/raw/my_python_project.zip
This file is decompressed into the /data/data/org.modrana.PySide.Example/ folder on first start after installation. Then /data/data/org.modrana.PySide.Example/main.py is run by Python.
To replace the example application, just replace the contents of my_python_project.zip, if you want to start other file than main.py, just change the MAIN_PYTHON_FILE path in main.h .
Replacing Python
The project contains two Python "bundles", one is used to compile the application wrapper and is located in build_dependencies/python, the other one is in {{android/res/raw/python_27.zip}}} and is deployed on first start after installation into /data/data/org.modrana.PySide.Example/python with all other bundled libraries and files in this archive.
When replacing Python, you should probably replace both bundles with the same Android-compiled Python version, or at least use the same series (2.7 & 2.7 not 2.7 & 2.6).
Replacing PySide libraries
The PySide libraries are located in android/res/raw/python_27.zip archive inside the lib folder. This folder is deployed to /data/data/org.modrana.PySide.Example/python/lib on the Android device.
When replacing PySide, you need to replace the libshiboken and libpyside:
lib/libshiboken.so lib/libpyside.so
the rest of the libraries is in the lib/python2.7/site-packages/PySide folder.
Replacing Qt Components
The Qt Components are packed in the android/res/raw/python_27.zip in the imports directory, the theme is in themes. These to folders are deployed like this after installation:
/data/org.modrana.PySide.Example/python/imports /data/org.modrana.PySide.Example/python/themes
So to replace Qt Components and/or their theme, just replace the content of the imports and/or themes folders in the python_27.zip archives.
Adding files, libraries & executables
Files
Arbitrary files needed by you application should probably go to the my_python_project.zip, to be deployed together with your application to the main instalation folder.
Libraries & executables
Libraries should be added to python_27.zip to the lib folder, exectuables to the bin folder. Like this they will be deployed to a folder that is listed in $LD_LIBRARY_PATH and $PATH respectively.
NOTE: I haven't yet tested if running executables through subprocess actually works.
Ideas for improvement
There is definitely still room for improvement, such as:
- a script that renames & customizes Necessitas Qt Cretor PySide projects
- building APKs from command line only without Qt Creator
- show a progress bar when the bundled libs are unpacked on first start
- modified bundling that doesn't unpack the files during startup bud during installation
- this could speed up the first start quite a bit
- compiling the many Qt Components files & images to a single resource file ?
- documenting how to use Android specific APIs from Python
- videos
Links
Source code listing
A convenient listing of sources for all the components used for the PySide & co port to Android. :)
Shiboken for Android
https://github.com/M4rtinK/shiboken-android/tree/android
PySide for Android
https://github.com/M4rtinK/pyside-android/tree/android
PySide for Android build scripts
https://github.com/M4rtinK/android-pyside-build-scripts
Qt Components
https://qt.gitorious.org/~martink/qt-components/martinks-ineans-qt-components/commits/android
Example program
https://github.com/M4rtinK/expyside/tree/android
Example project for Necessitas QtCreator
https://github.com/M4rtinK/android-pyside-example-project
Binary listing
List of relevant pre-build binaries
PySide libraries
http://modrana.org/platforms/android/pyside/
PyQt libraries
http://modrana.org/platforms/android/pyqt4/
Python 2.7 compiled for android - libs, executables & headers
http://www.modrana.org/platforms/android/python2.7/python2.7_for_android_v1.zip
Qt Components for Android
http://modrana.org/platforms/android/qt_components/qt_components_v1.zip
Cut-down Qt Components theme
http://modrana.org/platforms/android/qt_components/qt_components_theme_mini_v1.zip
Example application APK
http://modrana.org/platforms/android/pyside_example/PySideExample_1.1.apk
Acknowledgement
As usual with open source development, I haven't done all of this single handedly, but built on work done by others previously. So I'd like to both acknowledge on which work this is build upon and also provided links to the sources I've used:
- THPs PySide for Android - showing that this is possible
- Ssortagem@Github - integrated & improved THPs patches for Shiboken and PySide
- android-python27 - solved the APK bundling issue, provides Android-buildable Python 2.7
- the BlackBerry-Py Building PySide guide - I've used this as a base when making the Android build scripts
- Qt - provides the GUI toolkit :)
- PySide - for provides the Python-Qt bindings
Thanks a lot - without you, this would not be possible! :)
![(please configure the [header_logo] section in trac.ini)](/trac/chrome/site/nlp-logo.png)